The universe is a vast and fascinating place filled with mysteries that have captivated humans for centuries. From enigmatic black holes to the possibility of alien life, space holds secrets that challenge our understanding of science and inspire curiosity in people of all ages. In this family-friendly article, we’ll explore some of the most intriguing space mysteries, explain them in simple terms, and discuss what scientists are doing to uncover their secrets.
1. What Are Black Holes?
Black holes are among the most mysterious objects in the universe. They form when massive stars collapse under their own gravity, creating a region where gravity is so strong that nothing—not even light—can escape.
Scientists have discovered different types of black holes:
- Stellar black holes form from dying stars.
- Supermassive black holes sit at the centers of galaxies, including our Milky Way.
- Intermediate black holes are a rare type that falls between the other two categories.
One of the biggest mysteries about black holes is what happens inside them. The center of a black hole, called the singularity, is a point where gravity becomes infinite and space-time breaks down. Scientists use mathematical models to study these regions, but no one knows for sure what lies beyond the event horizon—the boundary around a black hole where escape becomes impossible[^1].
2. Are We Alone in the Universe?
The question of whether life exists beyond Earth is one of humanity’s greatest mysteries. Scientists search for alien life by studying planets outside our solar system, known as exoplanets.
To find habitable worlds, researchers look for planets in the “Goldilocks zone”—a region around a star where conditions are just right for liquid water to exist. NASA’s Kepler Space Telescope and its successor, the James Webb Space Telescope, have identified thousands of exoplanets[^2].
One intriguing candidate is Proxima Centauri b, an Earth-sized planet orbiting our closest neighboring star. While scientists haven’t found direct evidence of alien life yet, they continue to study atmospheres and chemical compositions to look for signs like oxygen or methane that might indicate biological activity[^3].
3. The Mystery of Dark Matter
When astronomers observe galaxies, they notice something strange: The stars within them move as if there’s far more mass than we can see. This invisible material is called dark matter, and it makes up about 27% of the universe[^4].
Dark matter doesn’t emit light or energy, which means scientists can’t see it directly. Instead, they detect its presence through its gravitational effects on visible objects like stars and galaxies.
Despite decades of research, scientists still don’t know what dark matter is made of. Some theories suggest it could be composed of exotic particles that interact weakly with ordinary matter[^5]. Experiments like CERN’s Large Hadron Collider aim to uncover its secrets by studying particle collisions at high energies.
4. What Are Fast Radio Bursts?
Fast Radio Bursts (FRBs) are mysterious flashes of radio waves coming from deep space. These bursts last only milliseconds but release as much energy as the Sun does in an entire day[^6].
FRBs were first discovered in 2007, and since then, astronomers have detected hundreds more using radio telescopes like Canada’s CHIME Observatory. Some FRBs seem to repeat from the same location, while others occur only once[^7].
What causes FRBs? Scientists think they might be produced by neutron stars (the dense remnants of supernova explosions), but other theories suggest exotic phenomena like magnetars or even advanced alien civilizations[^8].
5. The Enigma of Time Travel
Time travel has fascinated humans for centuries and often appears in science fiction stories. But is it possible according to science?
Einstein’s theory of relativity suggests that time isn’t fixed—it can stretch or compress depending on how fast you’re moving or how close you are to a massive object like a black hole[^9]. This means traveling into the future is theoretically possible if you move at near-light speeds or experience intense gravitational fields.
However, traveling into the past presents paradoxes (like changing events before they happen) that make it much harder to explain scientifically. While time travel remains a mystery, it continues to inspire both scientists and storytellers alike!
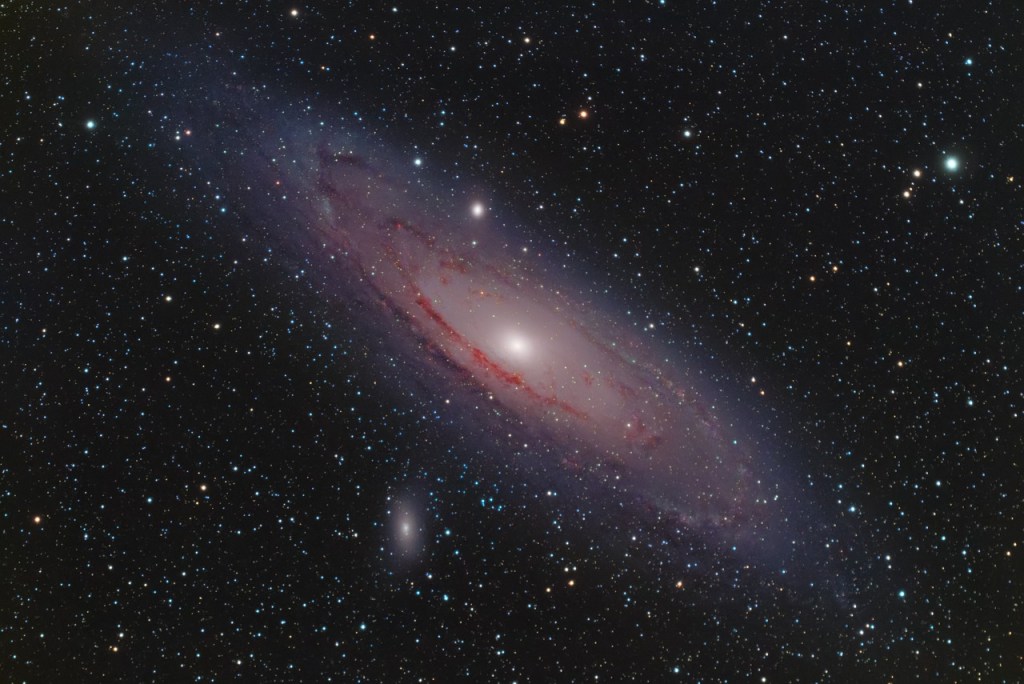
6. Why Do Galaxies Collide?
Galaxies are enormous collections of stars, gas, and dust held together by gravity—but they don’t stay still! Over billions of years, galaxies can collide and merge into larger structures[^10].
One famous example is the Andromeda Galaxy, which is on a collision course with our Milky Way Galaxy. In about 4 billion years, these two galaxies will merge into one giant galaxy called “Milkomeda”[^11].
Galactic collisions might seem chaotic, but they rarely result in star collisions because stars are so far apart relative to their sizes. Instead, these events create new star-forming regions and reshape galaxies’ appearances over time[^12].
7. The Mystery of Cosmic Inflation
The Big Bang theory explains how the universe began about 13.8 billion years ago—but scientists believe something extraordinary happened just moments after: cosmic inflation. During this period, the universe expanded faster than the speed of light[^13].
Why did inflation occur? Scientists don’t fully understand what caused this rapid expansion or why it stopped after such a short time (less than a trillionth of a second). Studying cosmic microwave background radiation—the faint glow left over from the Big Bang—helps researchers learn more about inflation’s effects on today’s universe[^14].
Fun Activities for Families
Want to explore space mysteries at home? Here are some engaging activities:
- Black Hole Simulation: Use marbles and bowls to simulate how objects fall into a black hole’s gravity well!
- Alien Planet Design: Create your own exoplanet with features like oceans or diamond rain (inspired by real discoveries).
- Dark Matter Hunt: Use flashlights and shadows to explain how invisible forces affect visible objects!
- Time Travel Debate: Discuss whether you’d rather visit the future or change history—and why!
Conclusion
Space mysteries remind us how vast and complex our universe truly is—and how much more we have yet to discover! Whether it’s black holes swallowing light or galaxies colliding over billions of years, each mystery challenges us to think bigger and ask deeper questions about existence itself.
As scientists continue exploring these phenomena with cutting-edge technology like telescopes and particle accelerators, we gain new insights into our cosmic origins—and perhaps even clues about our future among the stars! So grab your telescope or stargazing app tonight—you never know what wonders await just beyond Earth’s atmosphere!
References & Footnotes
[^1]: NASA Goddard Space Flight Center (2025). “Black Holes Explained.” https://www.nasa.gov/blackholes
[^2]: Kepler Mission Team (2025). “Exoplanet Discoveries.” https://kepler.nasa.gov/discoveries/
[^3]: James Webb Space Telescope Team (2025). “Proxima Centauri b Observations.” https://jwst.nasa.gov/observations/
[^4]: European Space Agency (2025). “Understanding Dark Matter.” https://www.darkmatter.eu/
[^5]: CERN (2025). “Particle Physics Experiments.” https://home.cern/science/darkmatterresearch
[^6]: CHIME Observatory (2025). “Fast Radio Burst Catalog.” https://chimeobservatory.org/frbs/
[^7]: Nature Astronomy Journal (2025). “Repeating FRBs.” https://nature.com/articles/frbs-repeating-patterns
[^8]: Harvard-Smithsonian Center for Astrophysics (2025). “FRB Origins.” https://cfa.harvard.edu/frb-research/
[^9]: Einstein Relativity Institute (2025). “Time Travel Possibilities.” https://einsteinrelativity.org/timetravel/
[^10]: Hubble Space Telescope Team (2025). “Galactic Collisions.” https://hubblesite.org/galaxies-colliding/
[^11]: NASA Science News (2025). “Milky Way-Andromeda Collision Course.” https://science.nasa.gov/milkomeda-future-galaxy/
[^12]: Space.com (2025). “Star Formation During Collisions.” https://space.com/star-formation-collisions/
[^13]: Planck Satellite Mission Team (2025). “Cosmic Inflation Studies.” https://planckmission.org/inflation-data/
[^14]: Astrophysical Journal Letters (2025). “Microwave Background Radiation Insights.” https://astrophysicaljournal.org/cosmic-background-radiation/