As the crisp autumn air settles in, November 2024 offers a spectacular array of celestial events for backyard astronomers of all levels. This guide will help novice stargazers navigate the night sky, highlighting key events and providing tips for optimal viewing. Remember, patience and persistence are key when exploring the cosmos.
Preparing for Your Stargazing Sessions:
- Choose a dark location away from city lights.
- Allow your eyes to adjust to the darkness for about 30 minutes.
- Use red light to preserve night vision when reading charts or adjusting equipment.
- Dress warmly, as November nights can be cold.
- Bring star charts, a compass, and a planisphere to help locate objects.
Now, let’s explore the celestial highlights for November 2024:
- New Moon – November 1

The month begins with a New Moon on November 1 at 4:49 am Alaska time. This is an excellent opportunity for deep-sky observation, as the absence of moonlight allows for optimal viewing of faint objects like galaxies and star clusters[4].
Tip for Novices: Use this dark night to familiarize yourself with constellations. Start with easily recognizable patterns like the Big Dipper or Orion, then use these as guideposts to explore further.
- Taurid Meteor Shower – Peak on November 4-5
The Taurids meteor shower, while minor, offers an interesting viewing opportunity. This long-running shower produces about 5-10 meteors per hour and consists of two separate streams[4].

Observing Tips:
- Best viewing will be just after midnight from a dark location.
- Look towards the constellation Taurus, but remember meteors can appear anywhere in the sky.
- Be patient, as this is not a prolific shower.
- Jupiter at Opposition – November 7
Jupiter reaches opposition on November 7, making it an excellent time to observe the gas giant. The planet will be at its closest approach to Earth and fully illuminated by the Sun[2].
Observing Tips:
- Look for Jupiter as a bright, non-twinkling “star” in the eastern sky after sunset.
- With binoculars or a small telescope, you may be able to see Jupiter’s four largest moons.
- A medium-sized telescope might reveal Jupiter’s cloud bands.
- Uranus at Opposition – November 17
Uranus reaches opposition on November 17, offering a rare opportunity to observe this distant ice giant[2].
Observing Tips:
- Uranus is barely visible to the naked eye under perfect conditions. Binoculars or a small telescope are recommended.
- Look for a tiny, blue-green disk in the constellation Aries.
- Use a star chart or astronomy app to help locate Uranus, as it’s not easily distinguishable from stars.
- Full Moon (Beaver Moon) and Supermoon – November 15
The Full Moon on November 15 is known as the Beaver Moon, Frosty Moon, or Dark Moon. It’s also the last of three supermoons for 2024, appearing slightly larger and brighter than usual[4].
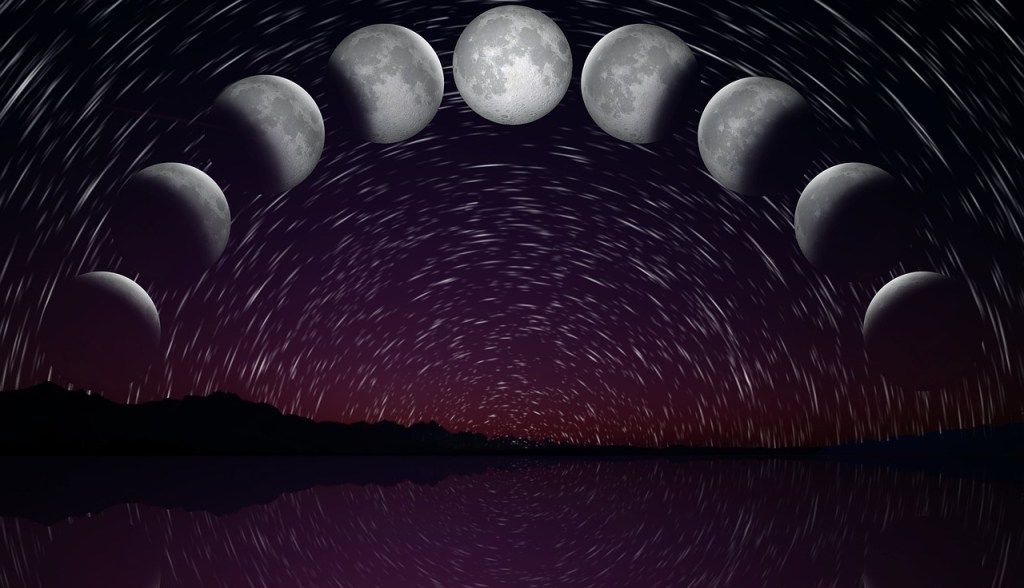

Observing Tips:
- The Full Moon rises around sunset and sets around sunrise.
- Use binoculars or a small telescope to observe lunar features, especially along the terminator (the line between light and dark).
- Try to spot the “Moon illusion” when it’s near the horizon, appearing larger due to an optical illusion.
- Leonid Meteor Shower – Peak on November 17-18
The Leonids meteor shower, while not as spectacular as some years, can still provide an enjoyable viewing experience. It typically produces up to 15 meteors per hour at its peak[2].
Observing Tips:
- The shower peaks on the night of November 17 and early morning of November 18.
- Look towards the constellation Leo, but remember meteors can appear anywhere in the sky.
- The best viewing is usually after midnight and before dawn.
- Mercury at Greatest Eastern Elongation – November 16
Mercury reaches its greatest eastern elongation on November 16, making it visible in the evening sky just after sunset[4].
Observing Tips:
- Look for Mercury low in the southwestern sky shortly after sunset.
- Use binoculars to help spot this elusive planet, as it’s often difficult to see with the naked eye.
- Don’t confuse Mercury with brighter Venus, which will be higher in the sky.
Check out these Beginner Telescopes
Constellation Highlights for November:
- Cassiopeia: This W-shaped constellation is high in the northeast.
Tip: Use Cassiopeia to find the Andromeda Galaxy (M31), our nearest large galactic neighbor. - Perseus: Look for this constellation below Cassiopeia.
Tip: Try to spot the Perseus Double Cluster with binoculars or a small telescope. - Taurus: The V-shaped face of the bull is prominent in the eastern sky.
Tip: Observe - the Pleiades star cluster (M45) within Taurus, visible to the naked eye but stunning through binoculars.
- Orion: Rising in the east later in the evening, Orion is one of the most recognizable winter constellations.
Tip: Use Orion’s Belt to find the Orion Nebula (M42), visible as a fuzzy patch below the belt.

Additional Tips for Novice Backyard Astronomers:
- Start with Naked-Eye Observing: Begin by identifying bright stars and constellations before moving on to binoculars or telescopes. This will help you learn to navigate the night sky.
- Use Star Charts or Apps: Familiarize yourself with the night sky using star charts or smartphone apps like Stellarium or Sky Map. These can help you identify objects and plan your observing sessions.
- Join an Astronomy Club: Local astronomy clubs often host star parties and can provide valuable guidance for beginners. They’re also a great way to meet fellow enthusiasts and learn from more experienced observers.
- Keep a Log: Record your observations, including date, time, and sky conditions. This can help you track your progress and remember what you’ve seen.
- Be Patient: Astronomical observing requires patience. Take your time and don’t rush from object to object. Allow your eyes to adjust and really soak in the views.
- Experiment with Astrophotography: Try capturing the night sky with your smartphone or camera. The Moon and bright planets can make great subjects for beginner astrophotographers.
- Learn to Star-Hop: Practice finding objects by using bright stars as guideposts. This skill will serve you well as you progress in your astronomical journey.
- Understand Light Pollution: Be aware of how light pollution affects your observations. Even in cities, you can often find darker areas in parks or on the outskirts of town.
- Maintain Your Equipment: Keep your optics clean and properly aligned. Learn basic maintenance for your binoculars or telescope to ensure the best views.
- Stay Safe and Comfortable: Always let someone know where you’re going if observing alone. Bring snacks, water, and extra layers to stay comfortable during long observing sessions.
Conclusion:
November 2024 offers a wealth of celestial wonders for backyard astronomers to explore. From the Taurid and Leonid meteor showers to the oppositions of Jupiter and Uranus, there’s something for everyone to enjoy in the night sky this month. The New Moon at the beginning of the month provides an excellent opportunity for deep-sky observing, while the Full Supermoon mid-month offers its own unique charm.
As you embark on your astronomical journey, remember that every night under the stars is an opportunity to learn and grow. Don’t be discouraged if you can’t immediately find or identify everything – astronomy is a lifelong pursuit, and there’s always something new to discover.
Take time to appreciate the vastness of the universe and our place within it. Stargazing not only offers a chance to learn about astronomy but also provides a unique perspective on our world and our place in the cosmos. It’s a hobby that can inspire wonder, foster curiosity, and provide a sense of connection to the universe around us.
So bundle up, grab your binoculars or telescope, and head outside to experience the magic of the November night sky. Who knows? You might just inspire the next generation of astronomers, astrophysicists, or space explorers. Happy stargazing!
Citations:
[1] https://spacetourismguide.com/november-night-sky/
[2] https://www.mestarocks.org/Celestial-Events-2024
[3] https://www.timeanddate.com/astronomy/sights-to-see.html
[4] https://www.uaf.edu/museum/education/educators/heliophysics-aurora-outre/astronomy-calendar/
[5] http://www.seasky.org/astronomy/astronomy-calendar-2024.html
[6] https://www.space.com/16149-night-sky.html
[7] https://getthekidsoutside.com/celestial-events-in-2024/
[8] https://earthsky.org/astronomy-essentials/visible-planets-tonight-mars-jupiter-venus-saturn-mercury/