Jupiter Largest planet in the Solar System
Basic Information
A gas giant, fifth from the Sun, with a mass more than two and a half times that of all the other planets in the Solar System combined.
Orbital Period – 11.86 Earth years
Distance from Sun – 5.20 AU (778.5 million km)
As the warm summer nights of July unfold, the celestial canvas above offers a spectacular array of wonders for stargazers of all ages. This month presents an excellent opportunity for families to embark on a cosmic adventure, exploring the marvels of the night sky together. From bright planets to dazzling constellations, the July night sky is a treasure trove of celestial delights waiting to be discovered.
Getting Started: Preparing for Your Stargazing Adventure
Before venturing out to explore the night sky, it’s essential to prepare adequately:
- Choose a dark location: Find a spot away from city lights for the best viewing experience. A local park or even your backyard can work well if it’s sufficiently dark.
- Allow your eyes to adjust: Give your eyes about 20-30 minutes to adapt to the darkness. This will significantly improve your ability to see fainter celestial objects.
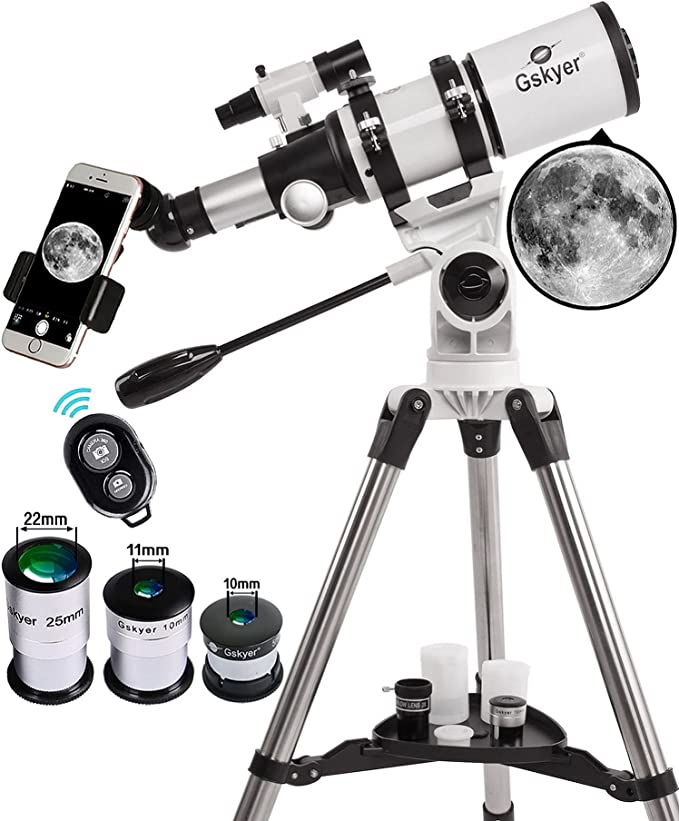
- Bring the right equipment: While many objects can be seen with the naked eye, a pair of binoculars can greatly enhance your viewing experience. A star chart or a smartphone app can also be helpful for identifying celestial objects.
- Dress appropriately: Even in July, nights can get chilly. Bring warm clothes and blankets for comfort during extended viewing sessions.
- Pack snacks and drinks: Stargazing can be a lengthy activity, so bring some treats to keep energy levels up.
Celestial Highlights for July
Planets on Parade

July offers excellent opportunities to observe several planets:
- Venus: The “Evening Star” shines brilliantly in the western sky after sunset. It’s the brightest object in the night sky after the Moon, making it easy for even the youngest stargazers to spot.
- Mars: The Red Planet can be seen in the western sky during the early evening hours. Its distinct reddish hue makes it stand out among the stars.
- Jupiter: Rising in the east during the late evening, Jupiter is a spectacular sight. With binoculars, you might even be able to spot its four largest moons.
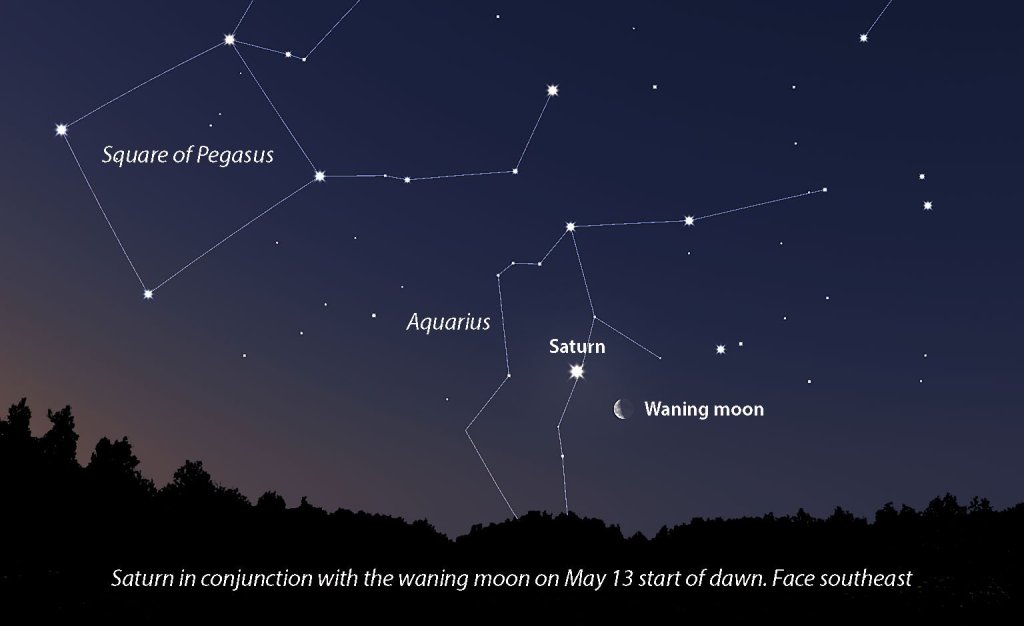
- Saturn: The ringed planet rises in the southeast as darkness falls. While its rings aren’t visible without a telescope, its golden hue is distinctive.
The Summer Triangle
One of the most prominent features of the July night sky is the Summer Triangle. This asterism (a pattern of stars that is not an official constellation) is formed by three bright stars:
- Vega in the constellation Lyra (the Harp)
- Deneb in Cygnus (the Swan)
- Altair in Aquila (the Eagle)
Challenge your family to spot this large triangle high in the eastern sky. It’s a great starting point for learning to navigate the night sky.
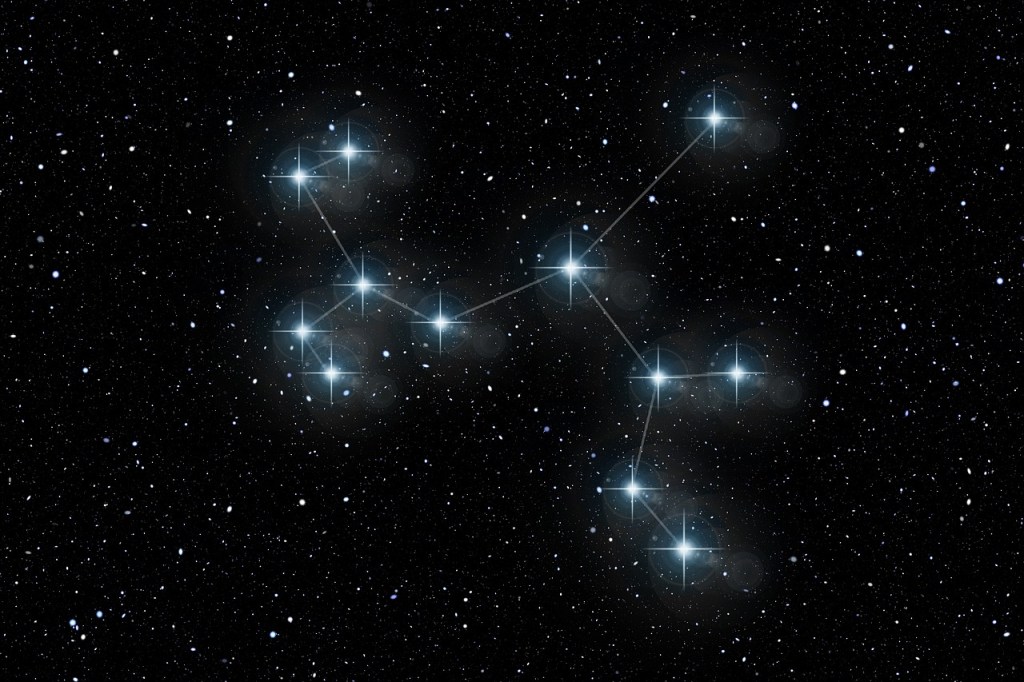
Locate your star locations with the star chart
The Milky Way
July provides an excellent opportunity to view our home galaxy, the Milky Way. On a clear, moonless night in a dark location, look for a faint, cloudy band stretching across the sky from the southern to the northern horizon. This is the combined light of billions of stars in our galaxy’s disk. Viewing the Milky Way can be a truly awe-inspiring experience for stargazers of all ages.
Constellations to Spot

July’s night sky features several prominent constellations:
- Scorpius (the Scorpion): Look for this distinctive constellation low in the southern sky. Its bright red star, Antares, marks the scorpion’s heart.
- Sagittarius (the Archer): Just east of Scorpius, Sagittarius is often visualized as a teapot. The center of our galaxy lies in this direction.
- Cygnus (the Swan): Also known as the Northern Cross, this constellation flies high overhead, with its bright star Deneb marking the tail.
- Ursa Major (the Great Bear): This large constellation, which contains the Big Dipper, is visible year-round in the northern sky.
Meteor Showers
While July isn’t known for major meteor showers, patient observers might spot a few “shooting stars” on any given night. The Delta Aquariids meteor shower begins in mid-July and peaks at the end of the month, offering a chance to wish upon a star!
Fun Activities for Family Stargazing
- Constellation Story Time: Many constellations have fascinating myths associated with them. Research these stories beforehand and share them as you identify the constellations in the sky.
- Star Hop Challenge: Use bright stars or constellations as starting points to “hop” to other celestial objects. For example, use the Big Dipper to find Polaris, the North Star.
- Moon Observation: If the Moon is visible, observe its phases and prominent features like craters and “seas” (large, dark plains).
- Satellite Spotting: Try to spot artificial satellites moving across the sky. The International Space Station is particularly bright and can be seen at specific times.
- Astrophotography: With today’s smartphone cameras, it’s possible to capture basic images of the Moon and bright planets. This can be a fun way to document your stargazing adventures.
Find the BEST Equipment HERE
Remember, patience is key when stargazing. Take your time, let your eyes adjust, and don’t rush from object to object. The joy of stargazing often comes from the peaceful contemplation of the cosmos and the shared experience with loved ones.
Exploring the July night sky as a family can be an enriching and bonding experience. It offers a unique opportunity to learn about the universe, spark curiosity, and create lasting memories. So this July, take advantage of the warm nights, head outdoors, look up, and embark on your own cosmic adventure. The wonders of the universe await!
Citations:
[1] https://www.theguardian.com/science/2017/may/28/the-june-night-sky
[2] https://www.planetary.org/night-sky/night-sky-what-to-see-this-month
[3] https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Jupiter
[4] https://www.space.com/16452-jupiters-moons.html
[5] https://www.britannica.com/place/Jupiter-planet